best exam test for meniscal tear|meniscus tear tests self : distributing You don’t need to do anything to prepare for a McMurray test. Just visit your provider as soon as possible if you’ve injured your knee or you notice any new . See more Portable, Top-loading Autoclaves With Advanced Safety and User-Friendly Features. Space-saving design with lid opening upward. Programmable auto-start for initiating a cycle up to 1 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
La temperatura en la cámara puede alcanzar la temperatura de esterilización de 121 ℃ mucho antes de que el líquido dentro del contenedor llegue a la misma temperatura. Y de forma opuesta sucede lo mismo. La . See more
The McMurray test is a series of movements to check your symptoms and range of motion (how far you can move your knee joint). The test is simple and includes the following steps: 1. You’ll lay on your back. 2. Your provider will bend your knee to 90 degrees perpendicular to the rest of your body (about where it . See moreYou don’t need to do anything to prepare for a McMurray test. Just visit your provider as soon as possible if you’ve injured your knee or you notice any new . See moreTry to relax while your provider is moving your leg and knee during a McMurray test. Because the McMurray test is a series of physical motions, make sure . See more
A McMurray test is usually a first step in treating your knee. If your provider feels or hears anything in your knee during a McMurray test, they’ll recommend either . See more
There are no risks to your knee from your provider performing a McMurray test. You might feel a little pain or discomfort during the test, but even if your meniscus . See moreMcMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. . The McMurray test is a series of knee and leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. It’s an in-office physical exam, which means your provider can perform it without any special equipment or a separate appointment.
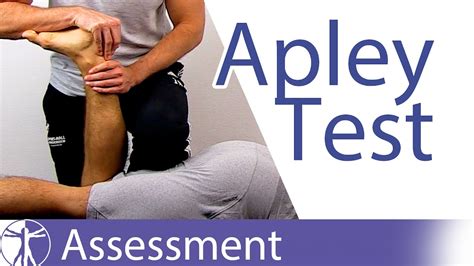
McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to be tested. Proximal Hand: holds the knee and palpates . Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive McMurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies. Ege's test helps diagnose a meniscus tear in the knee. It involves putting weight on the knee in a squatting position under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Pain or a clicking noise may indicate a meniscus tear. Your doctor may use other tests as well, including an MRI to confirm a diagnosis. The Thessaly test for detection of meniscal tears: validation of a new physical examination technique for primary care medicine. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(1):9-12. Email letter submissions to.
One of the main tests for meniscus tears is the McMurray test. Your doctor will bend your knee, then straighten and rotate it. This puts tension on a torn meniscus. If you have a meniscus tear, this movement may cause pain, clicking, or a clunking sensation within the joint.
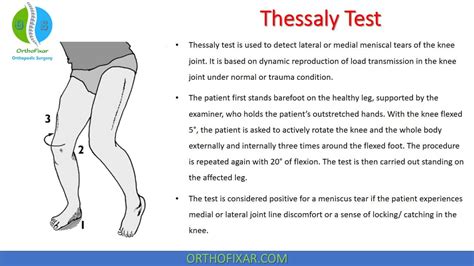
thessaly test for meniscal tear
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This uses a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of both hard and soft tissues within your knee. It's the best imaging study to detect a torn meniscus. Arthroscopy. In some cases, your doctor might use an instrument known as an arthroscope to examine the inside of your knee. A magnetic resonance imaging scan is considered the most accurate and noninvasive method of diagnosis. Meniscal tears are mainly either traumatic or degenerative. Small tears (<1 cm) are initially managed conservatively.
design and construction of an autoclave
Diagnosing meniscal tears involves a clinical exam, imaging (MRI), and sometimes arthroscopy to assess knee structure and determine the extent of injury.The Thessaly test is the most sensitive and specific clinical test to diagnose meniscal injury. Magnetic resonance imaging is first line for investigating potential meniscal lesions, but should not replace thorough clinical history and examination. The McMurray test is a series of knee and leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. It’s an in-office physical exam, which means your provider can perform it without any special equipment or a separate appointment.
McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to be tested. Proximal Hand: holds the knee and palpates . Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive McMurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies. Ege's test helps diagnose a meniscus tear in the knee. It involves putting weight on the knee in a squatting position under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Pain or a clicking noise may indicate a meniscus tear. Your doctor may use other tests as well, including an MRI to confirm a diagnosis.
special test for meniscal tear
The Thessaly test for detection of meniscal tears: validation of a new physical examination technique for primary care medicine. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(1):9-12. Email letter submissions to.One of the main tests for meniscus tears is the McMurray test. Your doctor will bend your knee, then straighten and rotate it. This puts tension on a torn meniscus. If you have a meniscus tear, this movement may cause pain, clicking, or a clunking sensation within the joint.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This uses a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of both hard and soft tissues within your knee. It's the best imaging study to detect a torn meniscus. Arthroscopy. In some cases, your doctor might use an instrument known as an arthroscope to examine the inside of your knee. A magnetic resonance imaging scan is considered the most accurate and noninvasive method of diagnosis. Meniscal tears are mainly either traumatic or degenerative. Small tears (<1 cm) are initially managed conservatively.
Diagnosing meniscal tears involves a clinical exam, imaging (MRI), and sometimes arthroscopy to assess knee structure and determine the extent of injury.

positive test for meniscus tear

design and construction of autoclave
design qualification autoclave
Autoclave is particularly useful for media-containing water that cannot be sterilized by dry heat. It is the method of choice for sterilizing the following: 1. Surgical instruments 2. Culture media 3. Autoclavable plastic containers 4. Plastic tubes and pipette . See more
best exam test for meniscal tear|meniscus tear tests self